NTC-07.23 “Basic electric drive”
Br0.00
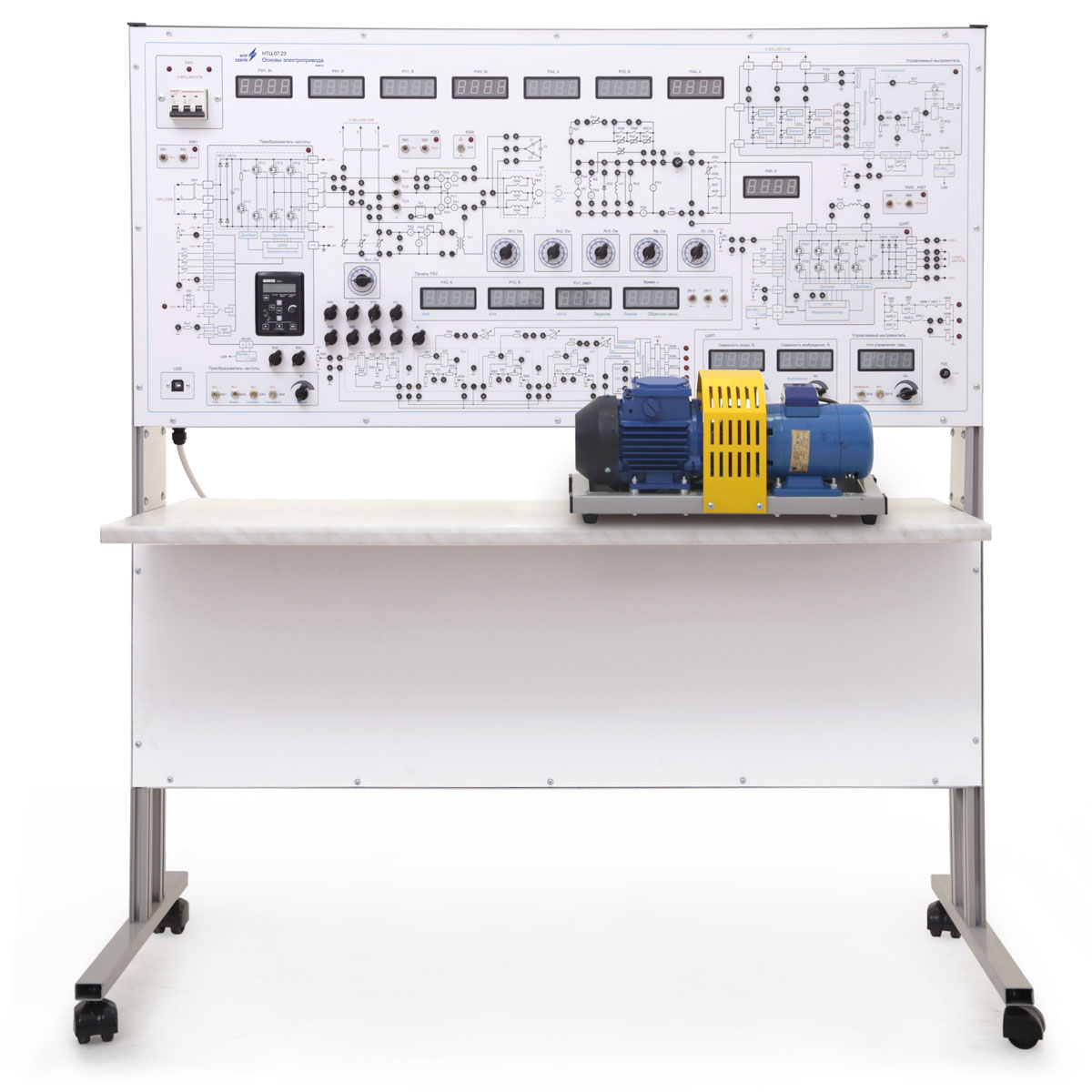
The educational laboratory stand is designed for use as training equipment in higher education, secondary specialized, and vocational-technical institutions. It is intended for conducting laboratory work to study automated electric drives, power conversion techniques, and drive control systems. The laboratory exercises include examining the characteristics and behavior of transformers, direct current motors (with independent and parallel excitation), asynchronous motors, generators, and their control systems. Special attention is given to determining static, dynamic, and regulation characteristics, energy diagrams, starting and braking methods, and the experimental determination of machine parameters. Various types of converters (controlled rectifiers, pulse-width modulation converters based on IGBT transistors), their components, software, and dynamic processes are also studied. Additionally, automatic regulation systems for speed, current, and voltage with open and closed control loops are analyzed, including subordinate regulation and positional control systems.
*For additional information, you can contact us via the phone numbers or email provided on the website.
 Русский
Русский